Ankylosing Spondylitis
Introduction
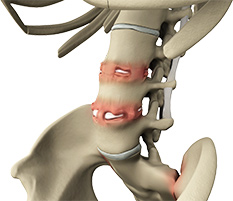
The term ankylosis refers to loss of mobility of the spine, whereas spondylitis means inflammation of the spine. Therefore, ankylosing spondylitis is a condition where chronic inflammation of the spine and sacroiliac joint results in complete fusion of the vertebrae leading to pain and stiffness in the spine. Sacroiliac joints are located in the lower back where the sacrum part of the vertebrae joins the iliac bones.
Ankylosing Spondylitis is a systemic disease affecting other tissues and organs throughout the body. It can cause inflammation of faraway joints and organs such as the eyes, heart, lungs and kidneys.
Ankylosing spondylitis is 3 times more common in men than in women and affects people of all age groups including children where the condition is referred to as juvenile ankylosing spondylitis.
Causes
The development of ankylosing spondylitis is believed to be genetically inherited as a majority of patients suffering from this condition are found to be born with a certain gene known as HLA-B27 gene. Other causative factors are family history, gender and certain environmental factors which can trigger immune system problems leading to chronic tissue inflammation.
Symptoms
The starting symptom of ankylosing spondylitis is pain and stiffness in the lower back which may get worse in the night or early morning. Back pain may be felt in the sacroiliac joint between the spine and pelvis. Progression of the disease can affect all or part of the spine resulting in decreased mobility of the lower spine and fatigue.
Other symptoms which are rarely seen include fever, loss of appetite, eye inflammation, and pain in heel, hip and other joints of the shoulders, knees, and ankles.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of ankylosing spondylitis involves a physical examination to evaluate the patient’s symptoms, X-rays and blood tests. Physical examination helps the physician assess stiffness and range of motion of the spine and other related joints. X-rays are ordered for a clear view of sacroiliac joints, vertebrae, and other related bones. Certain blood tests are employed such as HLA-B27 antigen, and sedimentation rate, which is a marker of inflammation throughout the body.
Treatment
The treatment of ankylosing spondylitis involves the use of certain medications to help reduce inflammation, suppress immunity, and prevent progression of the disease. Different classes of medications available for treatment include NSAIDs, corticosteroids, or other new classes having anti-inflammatory and pain-relieving effect.
Other treatment options are physical therapy and exercise. These are very effective measures that help alleviate many symptoms. Eat a healthy whole food diet and avoid drinking alcohol and smoking cigarettes.
In cases where severe damage of the joints or spine occurs, surgery can be performed.







